Roots blowers, also known as positive displacement blowers, are commonly used in various industrial applications for delivering a continuous flow of air or gas. There are primarily two types of Roots blowers:
Two-Lobe Roots Blower: This type of Roots blower consists of two lobes or rotors that rotate in opposite directions. The rotors have a unique shape resembling a figure-eight or “8.” The lobes are synchronized, creating a non-contacting operation with minimal internal clearance. Two-Lobe Roots blowers typically provide high flow rates at relatively low pressures.

Three-Lobe Roots Blower: The three-lobe Roots blower operates similarly to the two-lobe version but has an additional lobe. The three lobes are arranged with a 120-degree phase difference, resulting in smoother operation and reduced pulsations compared to the two-lobe design. Three-Lobe Roots blowers are often preferred for applications that require higher pressure ratios.
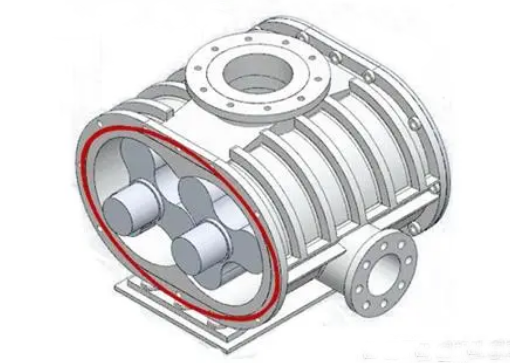
It’s worth noting that the Roots blower design has been around for many years, and variations or modifications in rotor profiles and geometries may exist, depending on the specific manufacturer or application requirements.


