Operating Principle of the Roots Blower
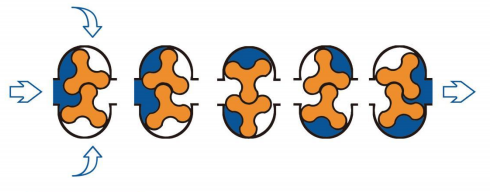
A roots blower consists of two rotors that compress gas, with the axes of the rotors parallel to each other. The rotor combines an impeller and shaft, and there are small gaps between the impeller and impeller, impeller and casing, and wall plate to prevent mutual contact and friction. The prime mover drives the two pairs of rotors through a pair of synchronous gears, causing them to rotate at equal speeds in opposite directions.
The impeller and casing enclose the blower’s inlet and outlet, and they form a closed primitive volume to convey gas effectively (as shown below).
Classification of Roots blowers
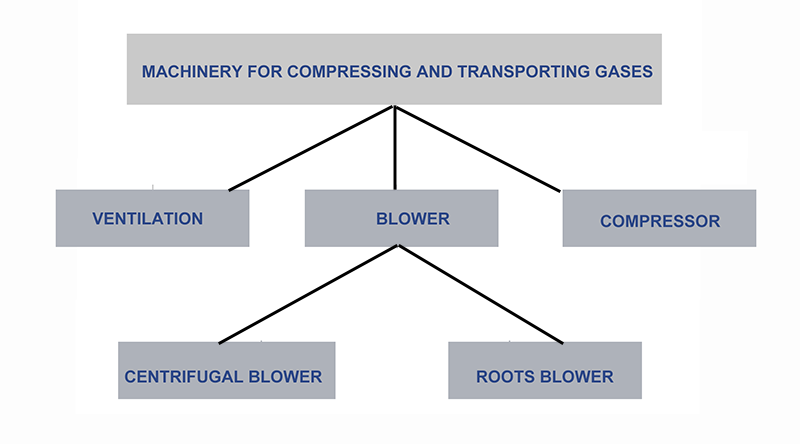
The machinery used for the compression and transmission of gas includes ventilation fans, blowers, and compressors. The purpose of the ventilation fan is primarily focused on transport, and it has a lower pressure. The compressor, on the other hand, has a higher pressure and its primary role is compression. The blower’s performance is between that of the ventilation fan and the compressor. The ventilation fan and blower are collectively known as fans.
Fans can be divided into two types: Roots blowers (positive displacement) and centrifugal blowers (turbine). Initially, Roots blowers were only used for positive pressure blowing, but they later expanded into the vacuum field and evolved into Roots vacuum pumps. When the inlet is at normal local atmospheric pressure, the exhaust pressure range is between 9.8200kPa. As a vacuum pump, the Roots blower can achieve a vacuum level of -9.8-80kPa when discharging directly to the atmosphere.
Although there is a nominal difference between a Roots blower and a Roots vacuum pump, they both operate near atmospheric pressure, and their pressure characteristics do not differ significantly. Usually, one can use Roots blowers directly as vacuum pumps for direct atmospheric discharge and vice versa.
Roots blowers and Roots vacuum pumps are divided into different categories based on their working methods. Single-stage and two-stage Roots blowers (vacuum pumps), dry and wet type are distinct based on their working intensity.
Classification of Roots Blowers
Single-stage and dual-stage
A Roots blower, which only has one compressor (one fan), is called a single-stage Roots blower. Two single-stage blowers that are connected in series to compress the gas twice in succession are called two-stage tandem blowers, or two-stage blowers for short.
Dry vs. wet type
The Roots blower is generally used for dry conveying. There are dry and wet type of Roots vacuum pumps. Wet vacuum pumps are mostly used at relatively high vacuum levels.
Other ways of classification
(1) According to the number of impeller heads, there are two-blade blowers and three-blade blowers.
(2) According to the structure arrangement, there are vertical blowers, horizontal blowers, intensive blowers, etc.
(3) According to the cooling method, air-cooled blowers, water-cooled blowers, counter-current cooling blowers, etc.
(4) According to the transmission mode, there are direct link blower, with link blower.
(5) According to the type of media, there are air blowers, gas blowers, hydrogen blowers, carbon dioxide blowers, etc.
(6) can also be divided according to the use of vertical kiln blower, gasification blower, aeration blower, oxidation fan, etc.


